
Digital pathology scanners transform diagnostics by providing high-resolution images, streamlining workflows, and enabling remote consultations, ultimately improving patient care.
The future of digital pathology looks promising, with ongoing advancements poised to further revolutionize the field:
Digital pathology scanners are revolutionizing medical diagnostics by enhancing accuracy, efficiency, and collaboration. As technology continues to advance, these tools will become increasingly integral to pathology practices worldwide, driving improvements in patient care and outcomes. Embracing digital pathology is not just an upgrade; it’s a leap forward in the quest for better healthcare.
The transition to digital pathology represents a paradigm shift in the field of medical diagnostics. By leveraging the power of digital imaging, AI, and telecommunication, pathologists can provide more accurate, efficient, and collaborative care. As we continue to innovate and integrate these technologies, the future of pathology promises to be more precise, personalized, and patient-centered.
Implementing digital pathology systems requires a significant initial investment in equipment, software, and training. However, the long-term benefits, such as improved efficiency, reduced diagnostic errors, and enhanced collaboration, often outweigh the upfront costs. Hospitals and laboratories should conduct a thorough cost-benefit analysis to determine the return on investment (ROI) and identify potential funding sources or grants.
Transitioning to digital pathology requires comprehensive training for pathologists, lab technicians, and support staff. Educational programs should cover the operation of digital scanners, software usage, data management, and best practices for digital pathology workflows. Continuous education and professional development are essential to keep pace with technological advancements and maintain high standards of diagnostic accuracy.
Managing and securing digital pathology data is crucial to maintaining patient confidentiality and complying with regulatory standards. Implementing robust data management systems, encryption protocols, and secure data storage solutions ensures the integrity and security of digital pathology records. Regular audits and compliance checks can help identify and address potential vulnerabilities.
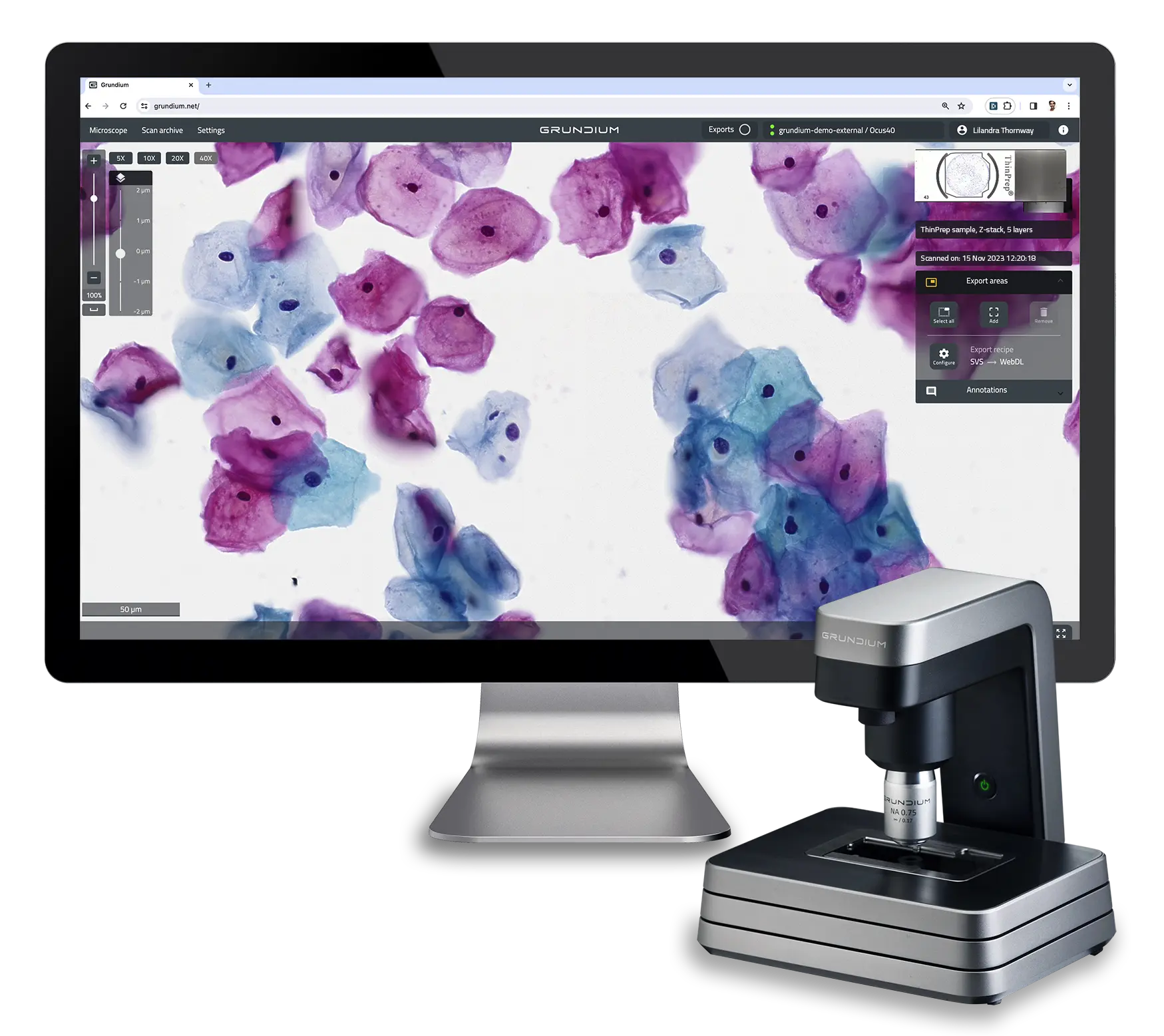
Digital pathology systems are designed with adaptability in mind, ensuring seamless integration into various workflows and laboratory environments. Modern digital pathology solutions, such as Grundium’s Ocus single-slide scanners, can often be integrated with laboratory information systems (LIS) and electronic health records (EHR), enabling efficient data exchange and reducing manual data entry. The flexible software solutions can be customized to fit specific laboratory needs, enhancing the overall efficiency of diagnostic workflows. This adaptability ensures that digital pathology systems can meet the diverse requirements of different pathology departments, from small clinics to large hospital laboratories. Collaborative efforts between IT departments, vendors, and pathology teams are essential for successful implementation and optimization.
Ongoing research and development in digital pathology focus on improving imaging technologies, developing advanced AI algorithms, and exploring new applications. Collaborative research initiatives between academic institutions, healthcare organizations, and technology companies drive innovation and accelerate the adoption of digital pathology solutions. Staying informed about the latest developments and participating in research projects can help organizations remain at the forefront of digital pathology advancements.
By addressing these considerations and adopting a strategic approach, healthcare organizations can maximize the benefits of digital pathology, improving diagnostic accuracy, efficiency, and patient care. As digital pathology continues to evolve, its integration into clinical practice will undoubtedly transform the landscape of medical diagnostics.

